What is light?
A burning candle has a soft, glowing flame that gives off light. But
when you turn on a light bulb, there is no flame. What makes the light
bulb give off light?
If you hold your hand above a light bulb, you’ll find a clue. The bulb
is hot! When the light is on, electricity runs through a tiny wire
inside the bulb. This makes the wire get hot. And when the wire gets hot
enough, something begins to happen.
Like everything else, the wire is made of atoms. And in the atoms there
are electrons. As the wires in the light bulb get hot, the electrons
soak up energy. And when they are loaded with energy, they throw it off.
The

bundles of energy thrown off by the electrons are light.
The bundles of energy have a special name. They are called photons
[(foh]{.smallcaps} tahnz). Photo is a word part that means \”light,”
and on at the end means \”a bit.” So photons are \”bits of light.”
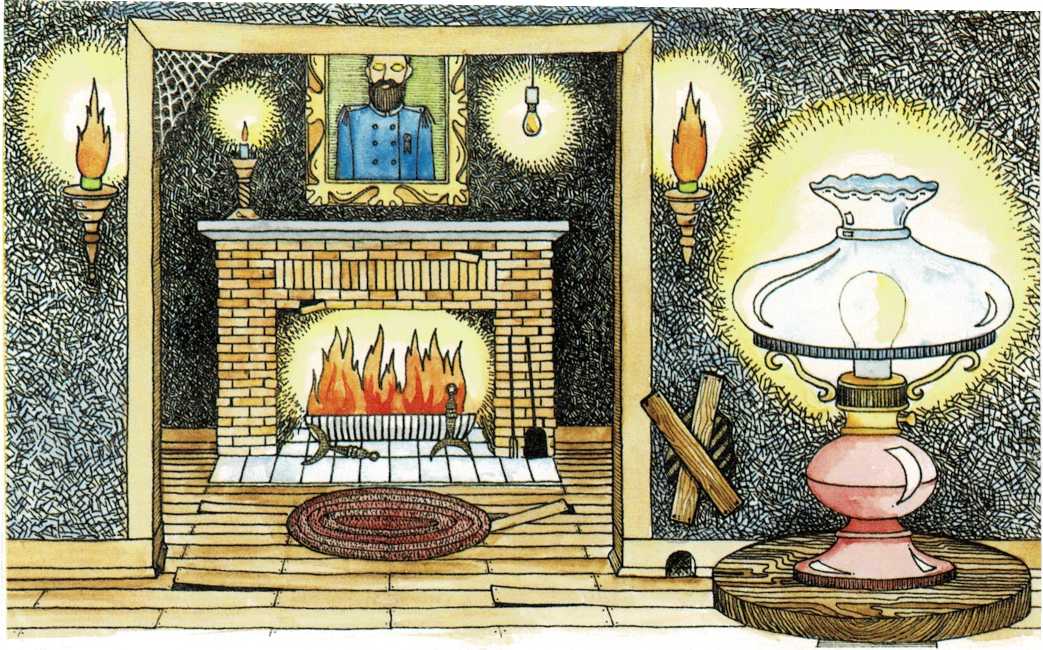
Anything that is hot enough—the tiny wire in the light bulb, a candle
flame, or a log fire—gives off light. And something as big and as hot
as the sun gives off a tremendous amount of light. The sun has a
temperature millions of times hotter than a light bulb, a candle flame,
or anything on earth. So the sun keeps its electrons jumping. And the
electrons keep pouring out bundles and bundles of light.