How does a gasoline engine work?
When a gasoline engine runs, matter is changed from one form to another,
and
Liquid gasoline flows through a pipe from the tank to the engine. On the
way, it passes through a special part that scoops in air. The
fast-moving air causes the gasoline to evaporate. It turns into a gas
and mixes with the air.
energy is released.
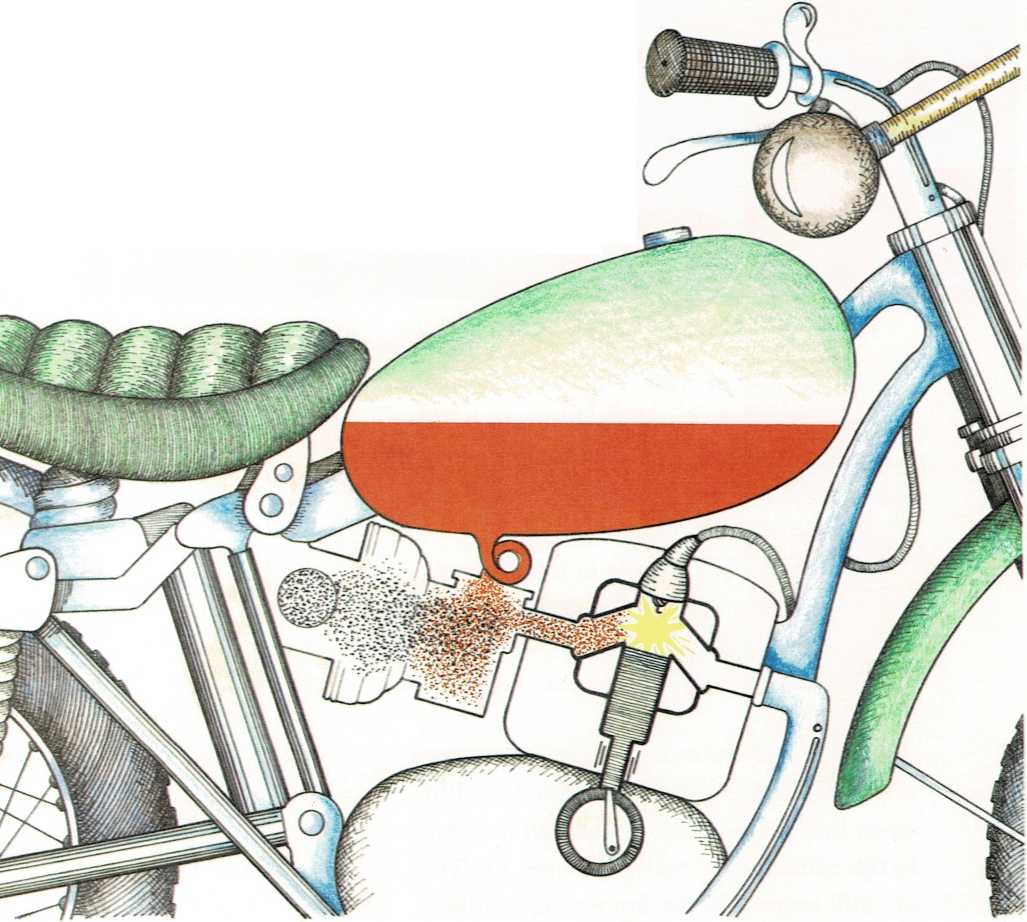
The gasoline-air mixture is pulled into the cylinders
[(sihl]{.smallcaps} uhn duhrz)—round openings inside the engine.
Inside each cylinder is a round part, called a piston
[(pihs]{.smallcaps} tuhn), that moves up and down.
As the piston moves up, it squeezes the gasoline-air mixture into the
top of the cylinder. Then a hot electric spark shoots into the mixture.
Bang! Instantly, the gas mixture burns. The heat is so fierce and sudden
that the molecules rush apart. This is an explosion. The force of the
explosion pushes the piston down. The piston pushes on other parts to
make them run. The noise you hear when a gasoline engine is running is
actually lots of these explosions, one right after another.
This is what happens in the engine of an automobile, a motorcycle, a
snowmobile, a lawn mower, and a snow blower. Matter is changed from one
form to another—and energy is released to make machines move!

