Swollen Glands
Swollen glands. Lymph glands (nodes) are one of the body’s means of
fighting infection. They are located throughout the body but are
especially concentrated in the neck, armpits, elbows, groin, abdomen,
and chest.
Location of the lymph glands
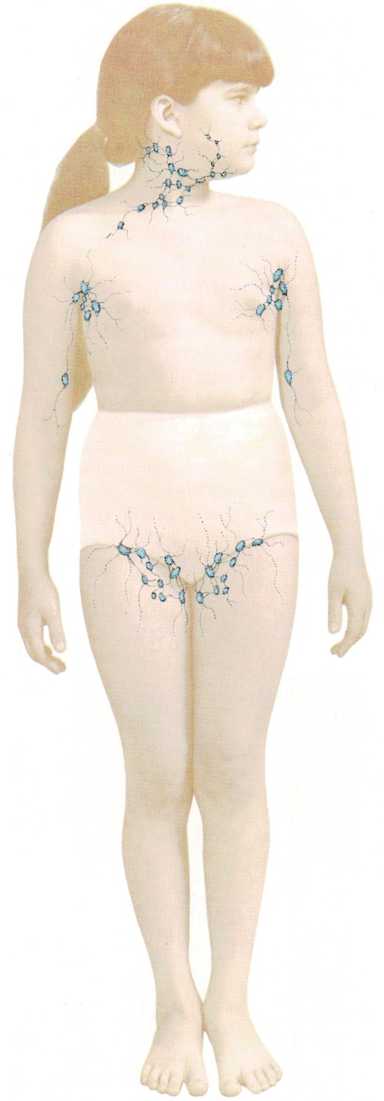
Lymph glands are located throughout the body. They swell to fight
off infection. Those in the neck, armpits, and groin can be felt when
they swell.
When an infection invades the body, the lymph glands collect and destroy
bacteria that drain from the infected area. Normally, the lymph glands
range in size from as small as a pea to as large as a plum. However,
when they are fighting an infection, they become enlarged and are known
as “swollen glands.”
* When the throat, tonsils, or gums are infected, lymph glands of the
neck swell. Mumps may cause lymph glands in the neck to swell.
When an infection occurs on the hands or arms, lymph glands in the
elbows and armpits swell.When an infection occurs on the leg or foot, lymph glands in the
groin swell.When vaccinations are given, lymph glands in the area of the shot
usually swell. ■ When measles, scarlet fever, or some other
infection affects the entire body, the lymph glands of the entire
body may swell. In some infectious diseases, like German measles and
mononucleosis, the lymph glands may remain quite large for some
time.
Leukemia, Hodgkin’s disease, and other malignant diseases of the
lymphatic system may also cause swollen glands. However, in most cases,
the child will have additional symptoms.
You can usually feel the lymph glands in the neck, armpits, and groin
when they are swollen. They may be inflamed and tender to the touch. If
your child has swollen glands, consult your doctor. Since the swelling
is most often caused by an infection, antibiotics are usually prescribed
to eliminate the infection. Sometimes, a lymph gland that is fighting an
infection forms an abscess. In such a case, hot packs on the swollen
gland may help to get rid of the abscess. Or, your doctor may have to
lance the abscess to release the pus. [m.g.]
See also Abscess; Adenoids; Communicable diseases; Fever;
Immunization; Leukemia; Mononucleosis; Sore throat; Tonsillitis

