Cancer – Canker Sores
Cancer is a disease in which there is a rapid, uncontrolled growth
of abnormal cells in the blood or other body tissue. The abnormal cells
destroy normal ones and take their place. Although cancer in children is
not common, it kills more children between the ages of 1 and 14 than any
other disease. Scientists do not yet know exactly what causes cancer.
If cancer attacks the blood, abnormal white blood cells are produced.
This condition is called leukemia. It is the most common type of cancer
in children. First signs of leukemia may include anemia, easy bruising,
bone pain, tiredness, loss of appetite, enlargement of lymph glands, and
prolonged and unexplained low-grade fever. Leukemia is no longer
uniformly fatal.
If cancer attacks the body tissue, it appears as a tumor (a lump or
swelling). Not
**
all tumors are cancerous. Those that are not are called benign tumors.
Cancerous tumors may occur anywhere in the body—the bones, the eyes,
the lymph glands, the muscles, the skin, the testes. Any lump or
swelling which can be seen or felt and which is growing rapidly may be a
sign of cancer. Other symptoms include weight loss, unexplained anemia,
unexplained fever, and failure to thrive.
Tumors of the brain may cause a child to walk unsteadily. They may also
cause severe headaches, repeated vomiting, convulsions, cross-eye,
double vision, and unconsciousness. Tumors of the spinal cord often
cause trouble with walking, stiffness of the back, or difficulties with
urinating.
Doctors use blood counts, X rays, computerized tomography (CT), magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI), radionuclide imaging, and bone marrow
examinations to diagnose cancer. Physicians may prefer to remove
tumors—both benign and cancerous—surgically. If the tumor is
cancerous, the surgeon often removes surrounding tissue to be certain of
removing all cancer cells. Otherwise, the cancer may begin to grow
again. Doctors also use radiation therapy and chemotherapy to help fight
cancerous tumors. The curing of a tumor depends on the type it is, where
it is located, and its stage of development, [m.g.]
See also Leukemia
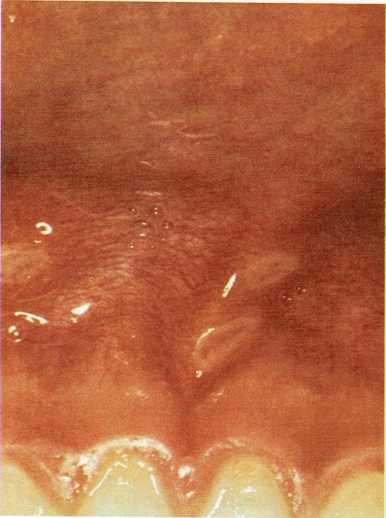
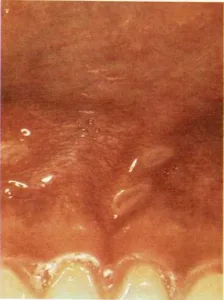
The gums are a common place for canker sores to develop.
The child may be able to drink nonirritating beverages such as apple
juice (avoid citrus juices) through a straw. After eating, the child
should use a mouthwash of plain water or salt water (one level
teaspoonful of table salt in a glass of water), [a.m.m.]
Canker sores are tender ulcers on the inside of the mouth. One or
several canker sores may develop at a time. Canker sores heal by
themselves slowly over a period of 8 to 12 days. Doctors do not know
what causes them.
Canker sores may first appear as tender, small blisters on the inside of
the cheeks, on the tongue, or on the gums. The child may complain of a
sore throat or refuse to eat or drink. After one oi\’ two days, the
blister breaks and a shallow, tender ulcer appears. During the first few
days, the child may have a fever (101° to 103° F.; 38° to 39.5° C). If
the child is uncomfortable, or a fever greater than 103° F. (39.5° C)
persists, give acetaminophen in age-appropriate doses. The glands below
the chin may become tender.
Car sickness. See Motion sickness
Carbon monoxide poisoning.
See Poisonings and poisons
Carbuncle. See Abscess; Boil