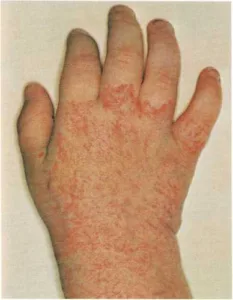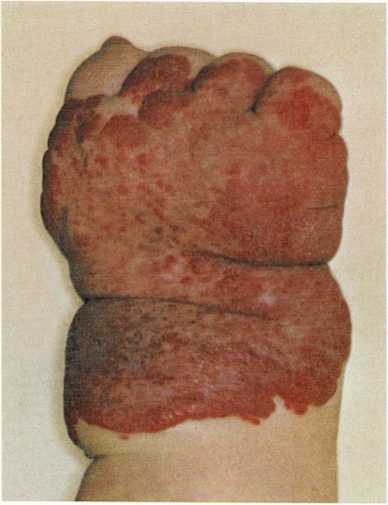
Some birthmarks (hemangioma) disappear by themselves. The baby shown
above was born with a birthmark on his hand and wrist.
Birthmark
Birthmark. Many children have birthmarks, but most birthmarks are
small and do not impair a child’s health in any way. Many disappear if
they are left alone. Others last throughout a person’s life.
Strawberry, or vascular, birthmarks are the most common. They are caused
by slightly enlarged or prominent blood vessels in the skin. Black or
brown birthmarks, often called moles, occur because of increased amounts
of pigment in the skin. If a new mole (nevus) appears, or if an old one
suddenly seems to be growing, bleeding, ulcerating or changing color, or
is painful, consult your doctor. The doctor will want to examine it to
be sure it is not harmful to the child’s health.
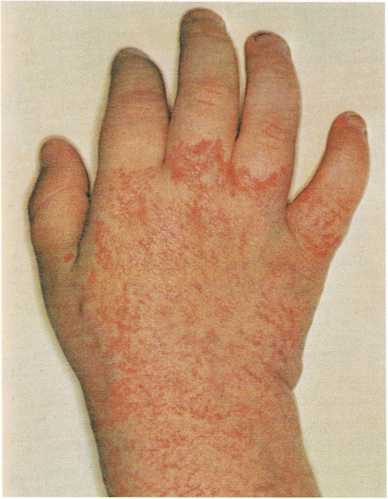
Three years later, the birthmark on the baby’s hand and wrist had
almost disappeared even though it was not treated in any way.
Salmon-patch birthmarks are light red or pink blotches commonly found on
the back of the neck, on the forehead, and on the eyelids. They usually
disappear by themselves during childhood.
Strawberry birthmarks are bright red, spongy in texture, and elevated
from the skin surface. Most of these birthmarks disappear by the time
the child reaches 3 to 5 years of age. But if one starts to grow
rapidly, consult your doctor. The doctor may treat strawberry birthmarks
by compression therapy. Occasionally, a doctor may remove the birthmarks
surgically.
Port-wine birthmarks are flat and purplish-red. They are commonly found
on the face or neck. A few may become lighter in time, but they rarely
disappear. You may wish to use a special cosmetic to cover them.
Mongolian spots are blue marks on the buttocks or lower back. They
usually disappear during childhood.
Some mothers of children with birthmarks wonder whether experiences or
thoughts they may have had during pregnancy could have caused the marks.
No evidence supports such a notion, [a m m]
See also Moles