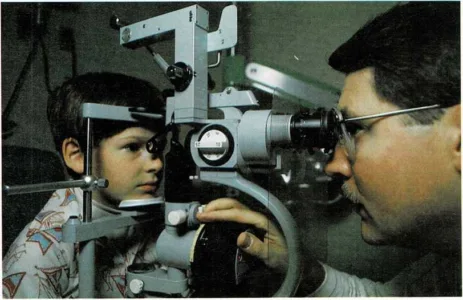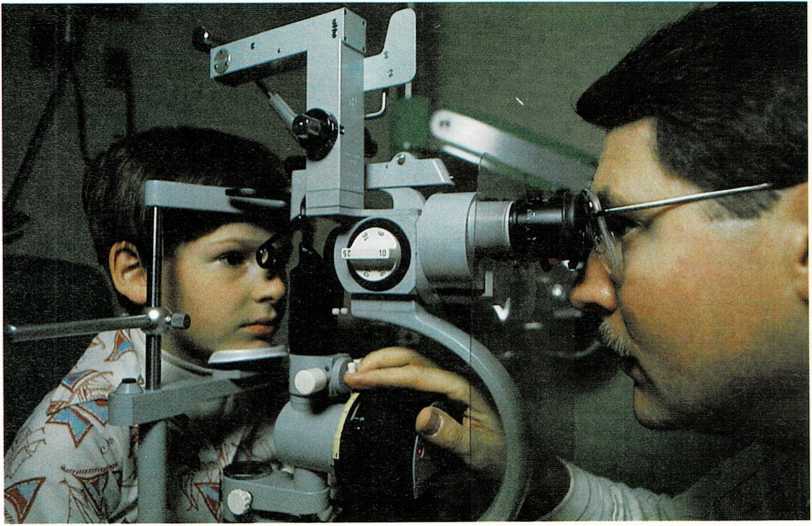
An eye examination is necessary to determine accurately whether or
not a child has astigmatism. Astigmatism can be corrected by glasses
or contact lenses.
Astigmatism – Ataxia
Astigmatism is a defect of the eye that makes images appear
distorted or blurred. It occurs when the lens or the cornea of an eye is
improperly curved. Because of this defect, not all the rays of light
from an object fall evenly on the retina. Some rays focus in front of
the retina, some on it, and some behind it. Both near-sighted and
farsighted eyes can be astigmatic. The condition is a common one and
seldom is a serious handicap. It can be corrected by glasses or contact
lenses. Eight out of 10 children have some degree of astigmatism.
Astigmatism is difficult, if not impossible, to diagnose without a
careful eye examination. But there are some signs that may indicate the
condition. Occasionally, in more severe forms, a child may hold the head
at an angle to make up for a blurred image. In milder forms, the
constant effort of the eye to overcome the irregularly blurred images
may result in headache, fatigue, irritability, or eyestrain,
[r.o.s.]
See also Eye health; Far-sightedness; Headache; Near-sightedness
Ataxia is a lack of muscle coordination. A child with ataxia moves
unsteadily and staggers when standing or walking. The child may turn
awkwardly and may frequently bump into objects such as tables and
chairs. All children have an ataxic gait when learning to walk, but
children who are developing normally should have a smooth gait by the
time they are 3 years old. If you suspect your child has ataxia, see
your doctor.
Ataxia usually indicates that the part of the nervous system that
controls balance and coordination is not functioning properly.
Here are some causes of ataxia.
Infection of the nervous system
A tumor in the nervous system
A hereditary disease that affects the nervous system
Accidental poisoning
Lead poisoning
Hysteria
Overdoses of sedatives, or of medicines that prevent convulsions or
vomiting, [a.g.s.]
See also Cerebral palsy; Hysteria
Athlete’s foot. See Ringworm