Communicable diseases. Most communicable diseases of childhood begin in much the same way. A child may wake up in the morning with a miserable case of sniffles, or may come dragging home from...
Colds – Coma
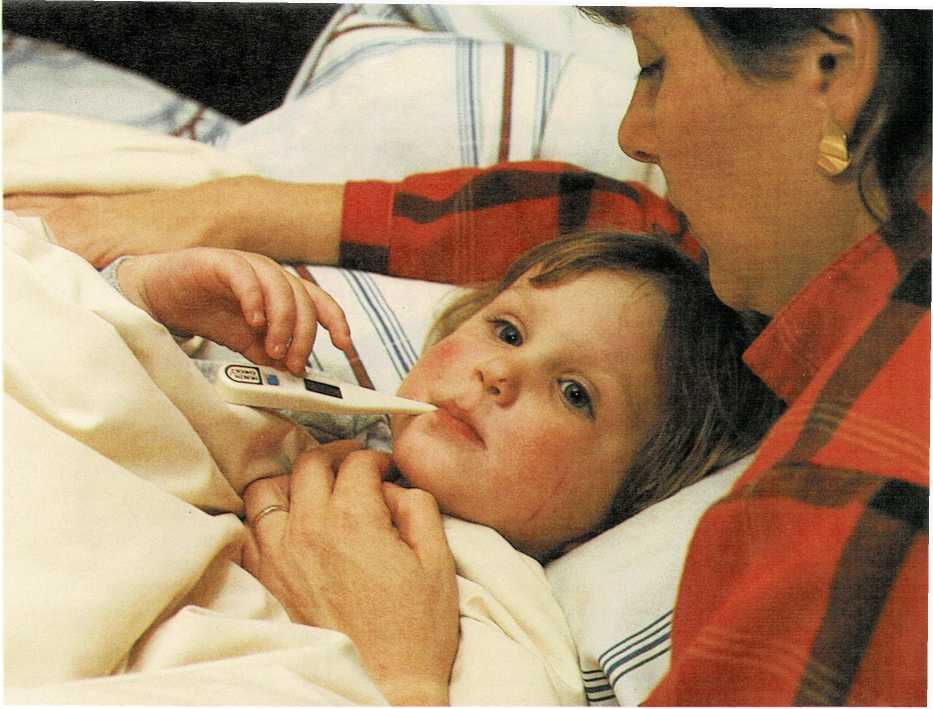
Colds. Sneezing, a stopped-up or runny nose, sore throat, and a cough usually are signs of the "common cold," a malady with which parents are all too familiar. Children under 2 years old usually get...
Cleft lip – Clubfoot
Cleft lip is a cleft (split) in the upper lip. It is congenital (present at birth). The cleft may be just a small notch on the lip or it may extend to one or both sides of the nose. A cleft lip may...
Choking – Chorea
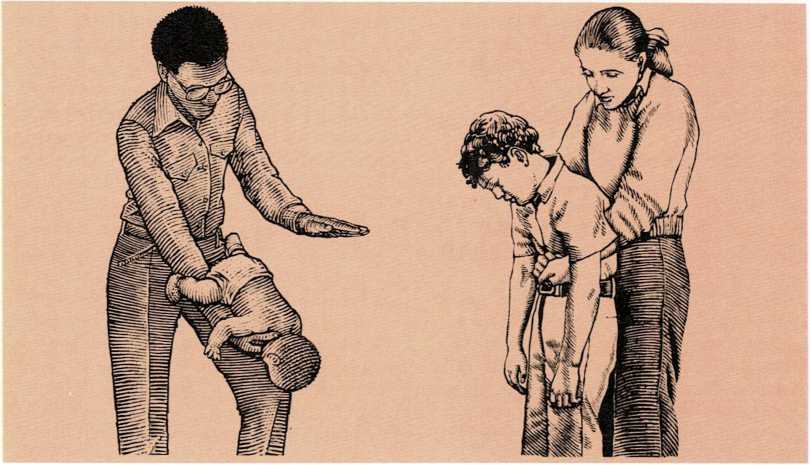
Choking. A child may choke from accidentally breathing food or other objects into the windpipe. If the child is coughing violently but can still breathe, go to the nearest hospital immediately. If...
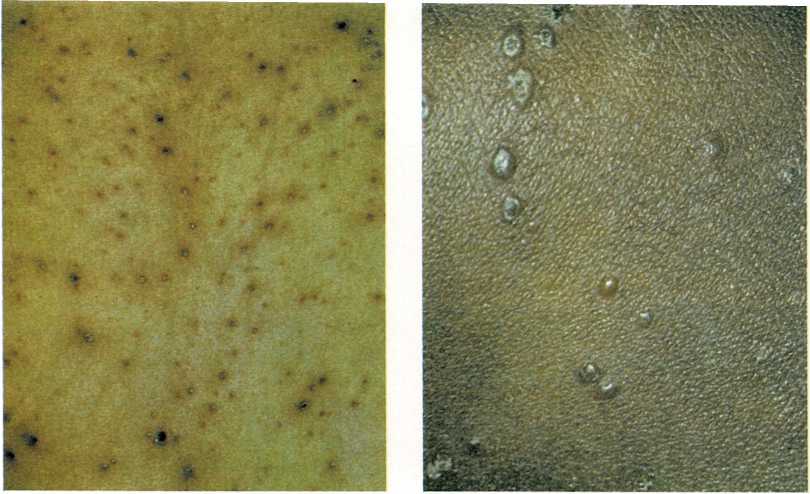
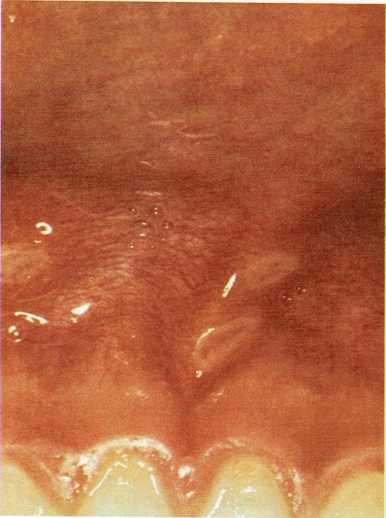
Cerebral Palsy – Chicken Pox
Cerebral palsy is a general term referring to a variety of motor disabilities that result from brain damage. The damage may occur before, during, or shortly after birth. Control of muscles and...
Cancer – Canker Sores
Cancer is a disease in which there is a rapid, uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the blood or other body tissue. The abnormal cells destroy normal ones and take their place. Although cancer...
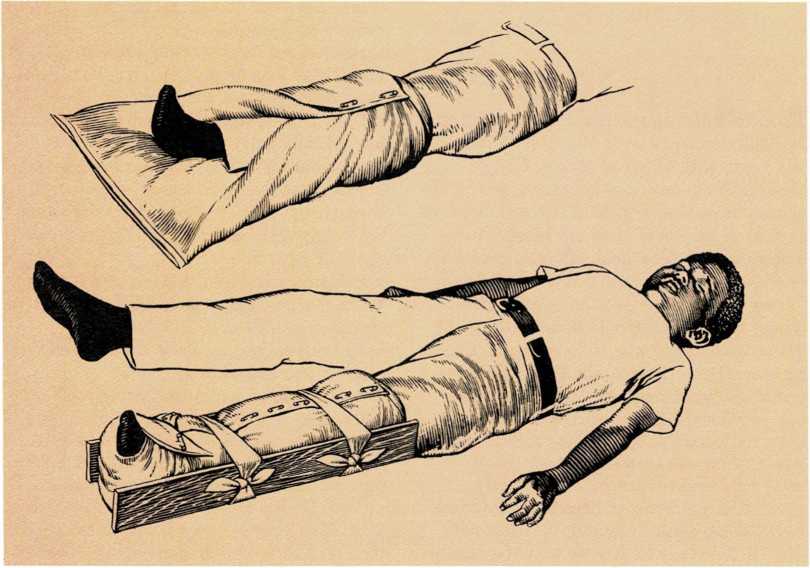
Broken Bones – Burns
Broken bones, also called fractures, are fairly common during childhood, particularly among boys. There are several types of fractures: - In a closed fracture, the broken bone does not cut through...
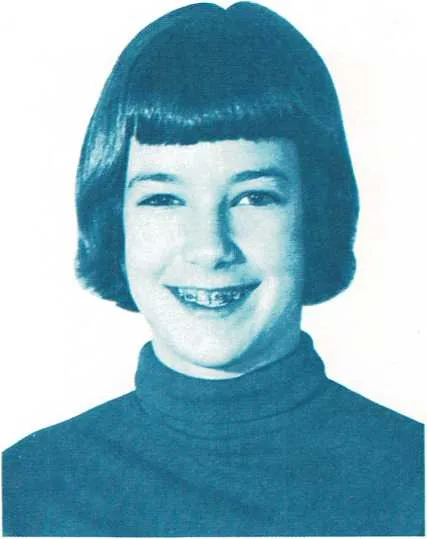
Braces, dental – Breath Holding
`Braces, dental`. If your child has malocclusion (poor bite), the dentist will probably suggest that you take the child to an orthodontist (a dentist who specializes in correcting irregularities...
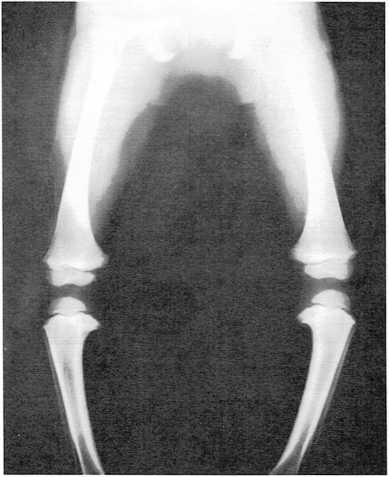
Boil – Bowlegs
Boil is a painful abscess under the skin that develops when a sweat gland, an oil gland, a small wound, or a hair follicle (the sac containing the hair root) becomes in fected and fills with pus....
Bleeding – Blood Type
Bleeding, if excessive, must be controlled promptly because it can be fatal. Stop excessive bleeding before you take precautions against infection. An infection can be treated later with...