The four seasons
Summer. Trees burst with thick loads of leaves. Flowers nod in soft,
warm breezes. Insects buzz. A blue sky holds a bright, hot sun.
Winter. Bare trees stand like bony skeletons against a cold, gray sky.
Snow blankets the ground. The sun seems pale and far away.
What causes this difference? Why is the earth warm in spring and summer
and cold in winter and fall?
Summer comes to your part of the world when a lot of the sun’s hot light
falls steadily upon it. Winter comes when not as much of the sun’s light
reaches your part of the world. Then, the ground and air cool off.


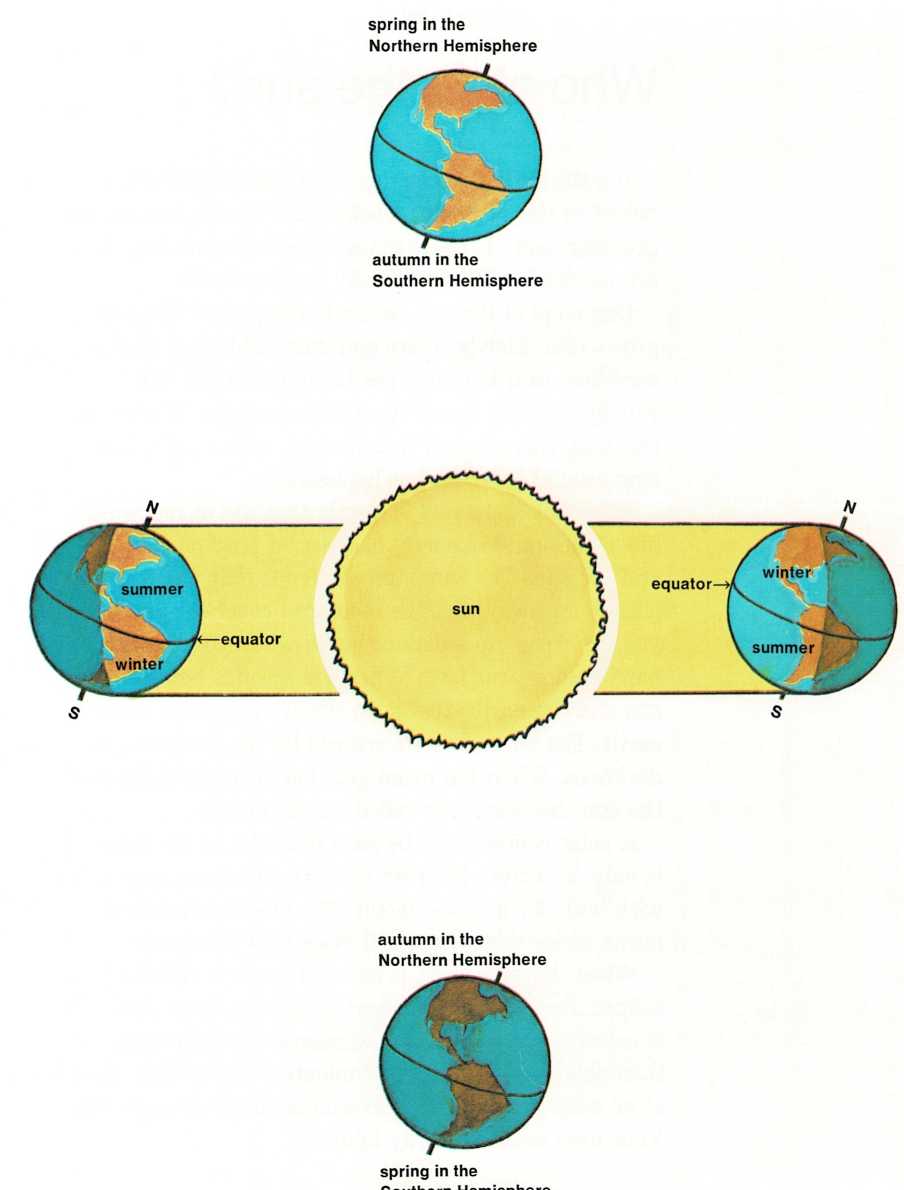
The difference in the amount of sunlight is caused by the tilt of the
earth. Earth’s North and South poles don’t point straight up and down,
they are tilted. Thus, when the earth is at one end of its path around
the sun, the North Pole is tilted toward the sun and the South Pole is
tilted away from the sun. Then, most of the sun’s light falls upon the
northern half of the world, keeping it warm. This causes summer. Because
the southern half of the earth isn’t getting as much light, it is cool.
This causes winter.
The earth moves on around the sun. When it has moved about one-fourth of
the way around, the northern part gets less light than it did, so it
grows cooler. This brings autumn to the north. The southern part gets
more light than it did, so it starts to warm up. This causes spring in
the south.
When the earth has moved halfway around the sun, the North Pole is
tilted away from the sun, and the South Pole is tilted toward the sun.
Now, the southern part of the world gets the most light and the northern
part gets the least. So, people in the northern part shiver in winter’s
cold, while those in the southern part enjoy summer.
One part of the earth always has summer. A band around the middle of
the earth, where the equator is, always gets about the same amount of
sunlight. So, it always stays hot.
ouuuierii ntuinapiieic